Configuration and Benchmarks of Peer-to-Peer Communication over Gigabit Ethernet and InfiniBand in a Cluster with Intel Xeon Phi Coprocessors
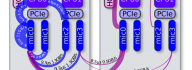
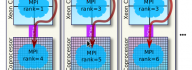
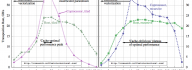
Intel Xeon Phi coprocessors allow symmetric heterogeneous clustering models, in which MPI processes are run fully on coprocessors, as opposed to offload-based clustering. These symmetric models are attractive, because they allow effortless porting of CPU-based applications to clusters with manycore computing accelerators. However, with the default software configuration and without specialized networking hardware, peer-to-peer communication between coprocessors in a cluster is quenched by orders of magnitude compared to the capabilities of Gigabit Ethernet networking hardware. This situation is remedied by InfiniBand interconnects and the software supporting them. In this paper we demonstrate the procedures for configuring a cluster with Intel Xeon Phi coprocessors connected with Gigabit Ethernet as well as InfiniBand interconnects. We measure and discuss the latencies and bandwidths of MPI messages with and without the advanced configuration with InfiniBand support. The paper contains a discussion of MPI application tuning in an InfiniBand-enabled cluster with Intel Xeon Phi [...]